Data Types in Java
Java is a statically typed language. Every variable must have a declared data type, which defines the kind of values it can store and the operations allowed on it.
-
Java has two broad categories: Primitive and Non-Primitive (Reference) data types.
-
Class fields (instance/static) get default values automatically, but local variables must be initialized before use.
-
Primitive values are stored directly; non-primitives store references to objects.
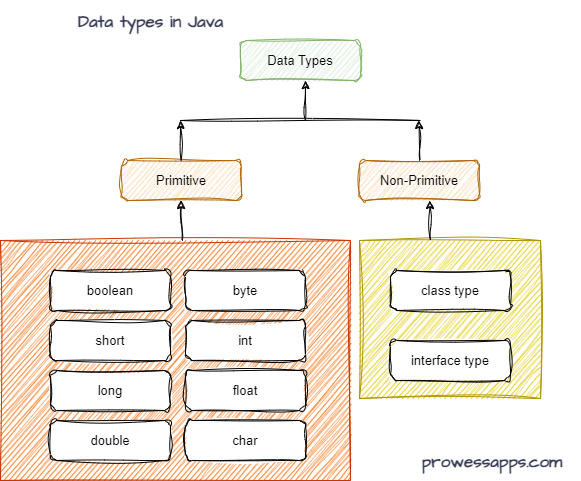
Primitive Data Types
Java provides eight primitive data types. They are predefined by the language and represented by reserved keywords.
| Data Type | Size | Default Value (for fields) |
|---|---|---|
| boolean | 1 bit | false |
| char | 2 bytes | '\u0000' |
| byte | 1 byte | 0 |
| short | 2 bytes | 0 |
| int | 4 bytes | 0 |
| long | 8 bytes | 0L |
| float | 4 bytes | 0.0f |
| double | 8 bytes | 0.0d |
Example: Default Values
public class DefaultValuesTest {
// Instance (non-static) primitives
byte b; short sh; int a; long l;
float f; double d; char ch; boolean bool;
// Static field
static int x;
// Reference type
String s;
void showValues() {
System.out.println("Default Value of byte b : " + b);
System.out.println("Default Value of short sh : " + sh);
System.out.println("Default Value of int a : " + a);
System.out.println("Default Value of long l : " + l);
System.out.println("Default Value of float f : " + f);
System.out.println("Default Value of double d : " + d);
System.out.println("Default Value of char ch : " + ch);
System.out.println("Default Value of boolean bool : " + bool);
System.out.println("Default Value of static int x : " + x);
System.out.println("Default Value of reference String s : " + s);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
DefaultValuesTest ob = new DefaultValuesTest();
ob.showValues();
}
}
Output:
Default Value of byte b : 0 Default Value of short sh : 0 Default Value of int a : 0 Default Value of long l : 0 Default Value of float f : 0.0 Default Value of double d : 0.0 Default Value of char ch : Default Value of boolean bool : false Default Value of static int x : 0 Default Value of reference String s : null
Notes
- Default values apply to fields (instance/static) only; local variables must be initialized.
booleanhas only two values:trueandfalse(no 0/1 shortcuts).- The default for a reference (e.g.,
String) isnull.
🚀 Quick Knowledge Check
Topic: Data-types | Language: Java
Q1. Which data type is used to store a single character in Java?
Q2. Which of the following is NOT a primitive data type in Java?
Q3. What will be the output of this code?
double a = 10/4;
System.out.println(a);Q4. What is the default value of a boolean variable in Java?
Q5. What will be the output of the following code?
int x = 130;
byte y = (byte) x;
System.out.println(y);